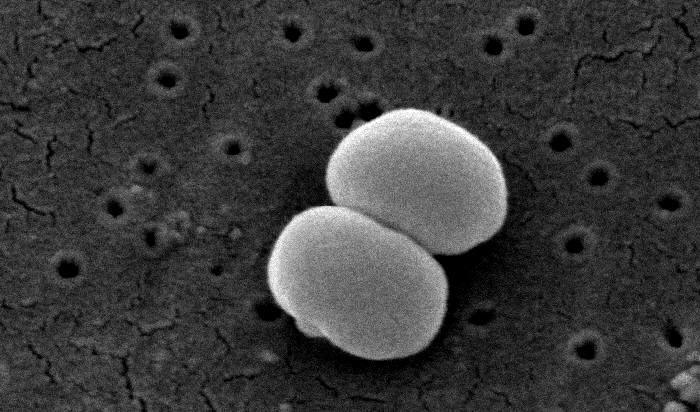
Staphylococcus Epidermidis Wikipedia

Staphylococcus Epidermidis Bacteria Microscopic Photography Things Under A Microscope Microscopic
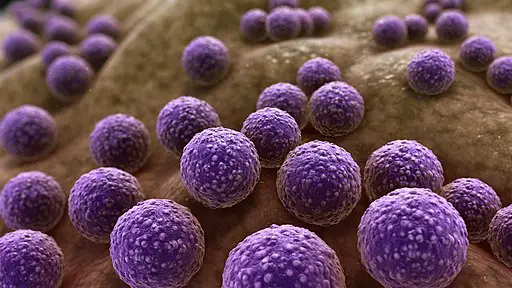
Staphylococcus Bacteria Examples Classification And Characteristics
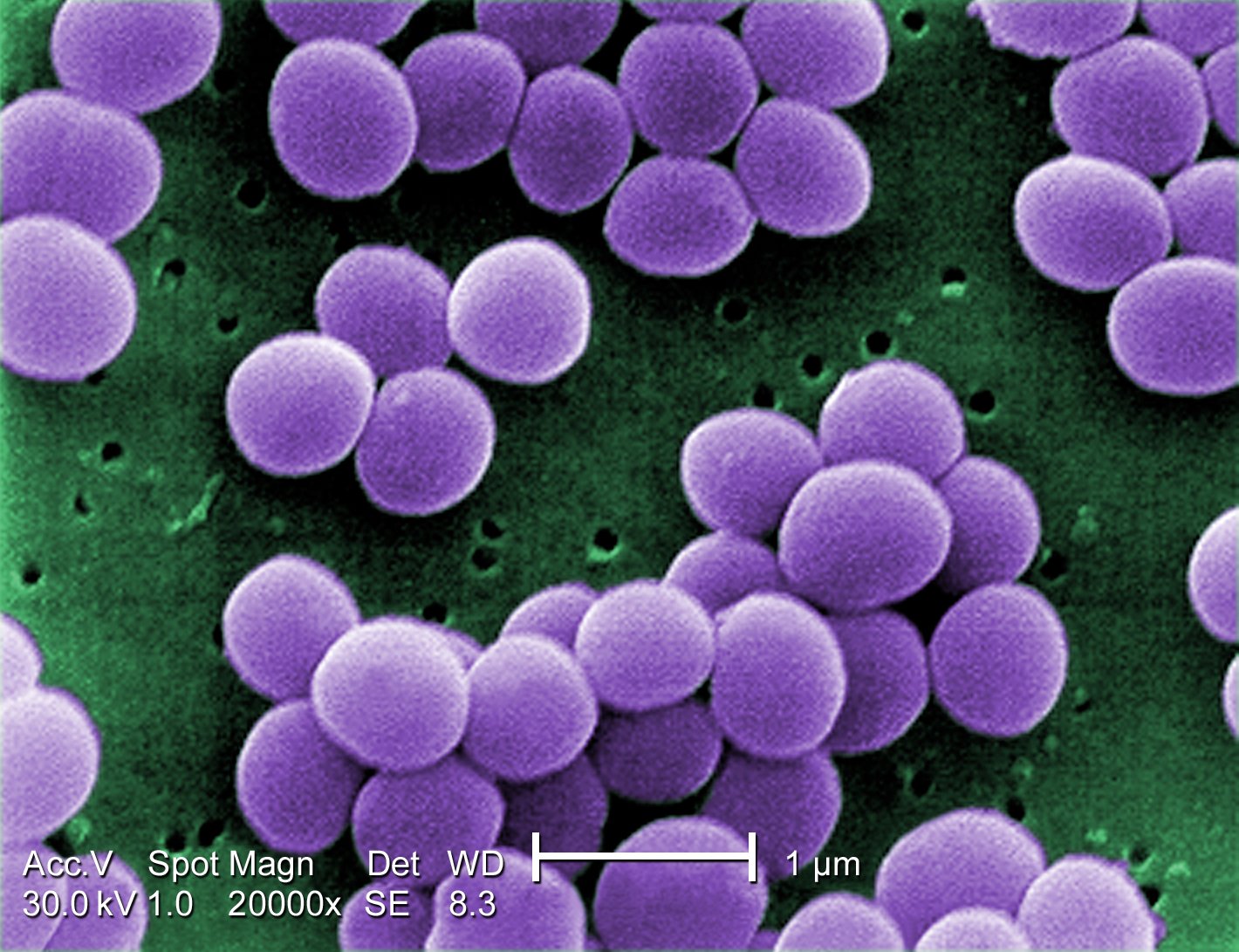
Bacteria Definition Types Infections Live Science
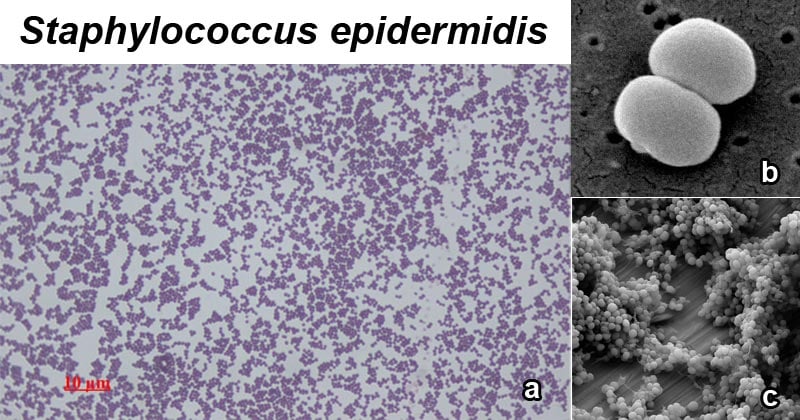
Staphylococcus Epidermidis An Overview Microbe Notes
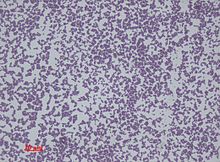
Staphylococcus Epidermidis Wikipedia
He is also to be found on foods and settled on polymeric surfaces.
Staphylococcus epidermidis بكتيريا. Staphylococcus equorum Schleifer et al 1985 Species. Apply to the affected area up to 3 times a day for 10 days. Not more than 10 days.
Epidermidis is often found as contaminant of clinical samples. These infections are often long lasting and difficult to treat due to the production o. In addition many humans carry strains of this bacteria on their skin nose and pharynx as harmless.
These gram-positive sphere-shaped coccal bacteria see figure How Bacteria Shape Up often cause skin infections but can cause pneumonia heart valve infections and bone infections. Dec 22 2019 Staphylococcus epidermidis 27 F S Staphylococcus saprophyticus 3 F Media in category Staphylococcus. Coagulase-negative staphylococci CNS are an essential part of the commensal flora of the human and other warm-blooded animals skin and mucous membranes.
It is part of the skin flora of humans and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae perineum and inguinal areas. The introduction of the drug is recommended to continue for another 2-3 days after normalization of body temperature and symptoms disappear. Staphylococcus epidermidis is a gram-positive coagulase negative hemolytic.
It is non-pathogenic in most circumstances. This organism can grow as a biofilm enhancing its ability to glide over surfaces such as catheters. What is Staphylococcus Epidermidis.
Epidermidis -related infections are acquired in hospitals and are associated with the use of medical devices 2. Christensen GD Simpson WA Bisno AL Beachey EH. Epidermidis has long been considered nonpathogenic it is now recognized as a relevant opportunistic pathogen 1.
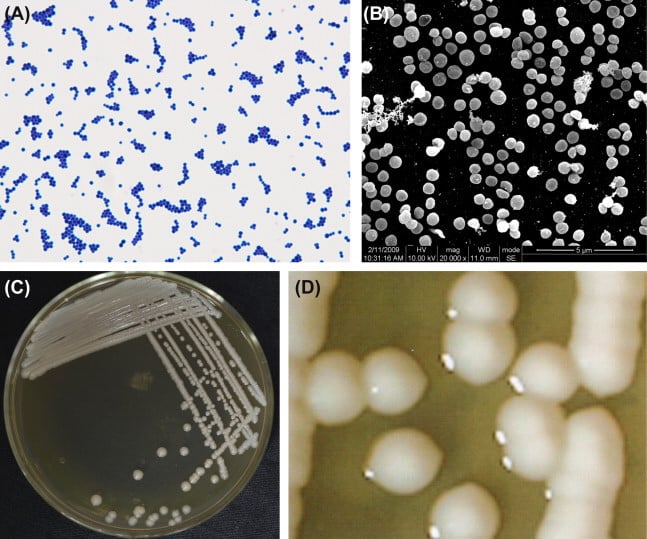
Staphylococcus Epidermidis An Overview Microbe Notes
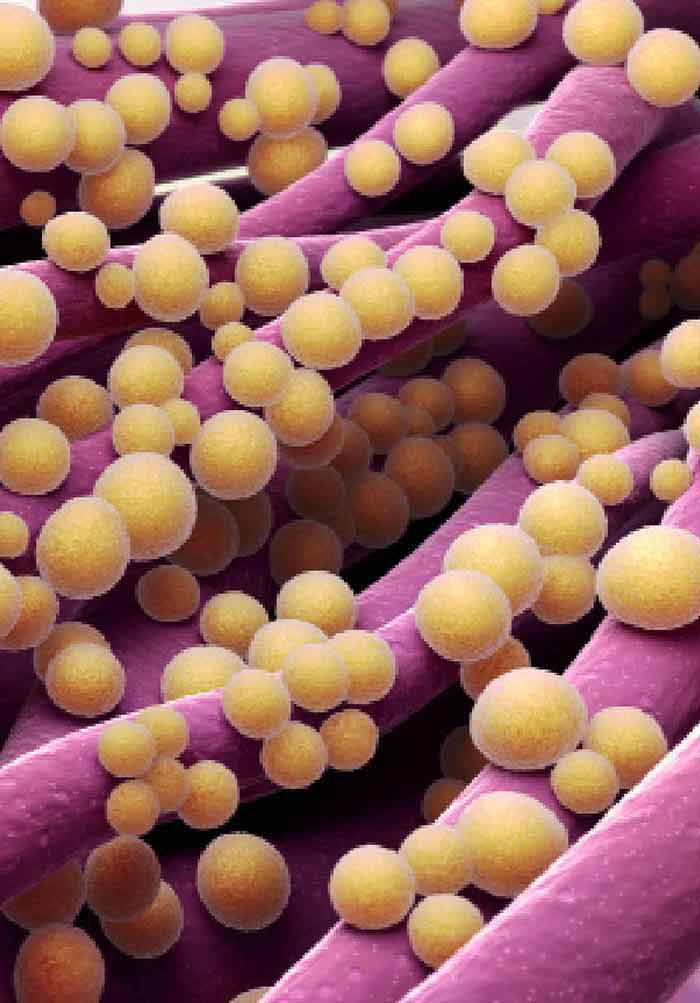
Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms And Their Impact On The Medical Field Intechopen

Staphylococcus Epidermidis Wikipedia
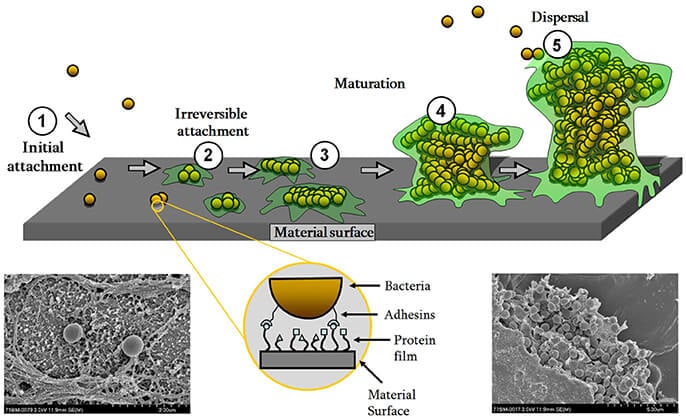
Staphylococcus Epidermidis An Overview Microbe Notes
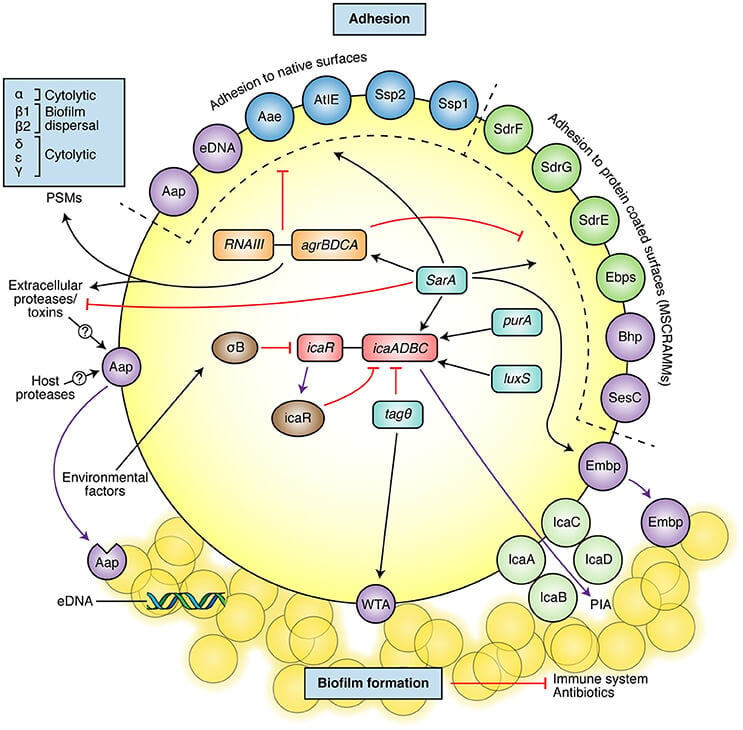
Staphylococcus Epidermidis An Overview Microbe Notes
Staph Epidermidis And Saprophyticus

Staph Epidermidis And Saprophyticus

Staphylococcus Bacteria Genus Britannica

Staphylococcus Epidermidis Wikipedia

Staphylococcus Epidermidis 1 000x 1 Microbiology Microbiology Lab Medical Laboratory Scientist

Pin On Sciart Microscopy Images

Pin On Your Every Day Yoga
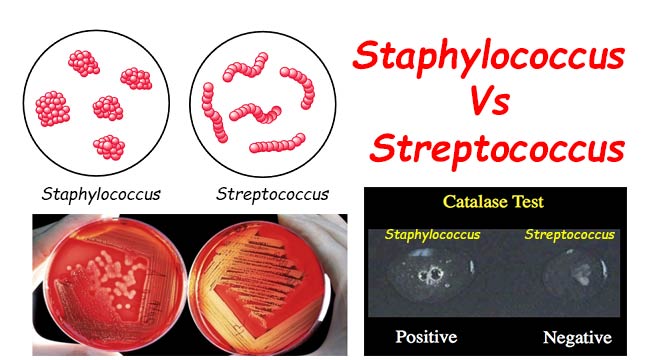
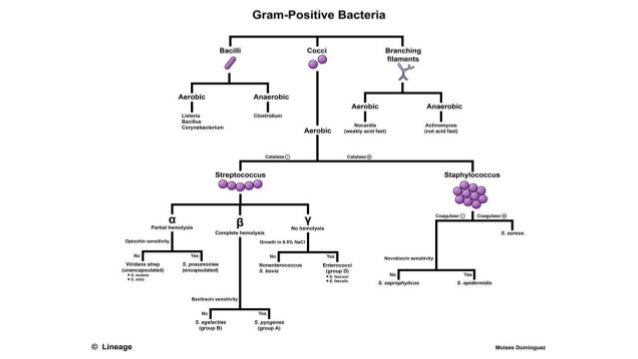
Differences Between Staphylococcus And Streptococcus Microbiology Info Com
 كونتنت موقع كونتنت يقدم العديد من المقالات في مجالات مختلفة
كونتنت موقع كونتنت يقدم العديد من المقالات في مجالات مختلفة